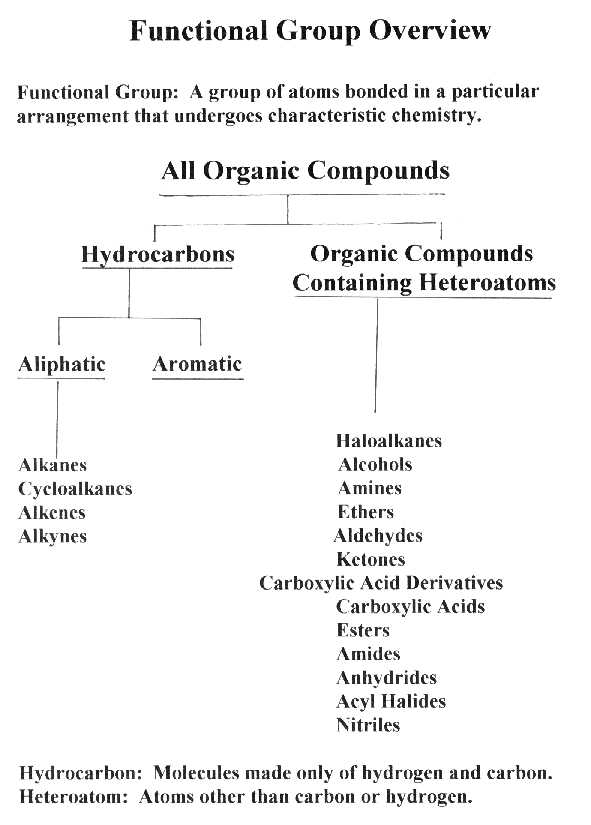
Functional Group
Overview Continued -
Specific Examples
1. Alkanes :
General Formula CnH2n+2
Examples:
|
CH4 |
CH3CH3 |
|
|
|
methane |
ethane |
propane |
octane |
Write the structure of decane:
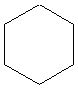
2.
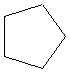
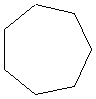
Cycloalkanes: General Formula
CnH2n
Examples
|
|
|
|
|
cyclopropane |
cyclopentane |
cycloheptane |
What is the name of the following compound?
3. Alkenes:
General Formula CnH2n
Examples:
|
|
|
|
|
ethene(ethylene) |
2-butene |
1-decene |
Write the structure of 2-pentene.
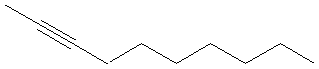
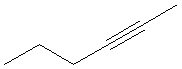
4. Alkynes:
General Formula CnH2n-2
Examples:
|
|
? |
|
|
Ethyne (acetylene) |
3-hexyne |
2-decyne |
What is the name of the following compound?
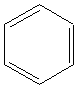
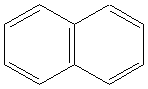
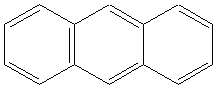
5.Aromatics:
Examples
|
|
|
|
|
benzene |
napthalene |
anthracene |
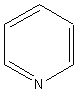
|
|
||
|
pyridine |
||
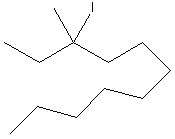
6. Haloalkanes
(alkyl halides):
Examples:
|
|
? |
|
|
Chloroethane 1o |
2-bromopentane 2 o |
3-iodo-3methylundecane 3 o |
The order of a
haloalkane and an alcohol has to do with the number of carbons directly
attached to the carbon bearing the
heteroatom. If that carbon has three carbons the haloalkane
(or alcohol) is 3 o or
tertiary , if it has two carbons it is 2 o or secondary , etc. It is noteworthy that carbons in alkanes can be designated
similarly. There is even a designation
4 o or quaternary for a
carbon bearing four directly attached
carbons. These designations are useful
when communicating specific information about regions of the molecules. There is also a variation in reactivity that
relates to order.
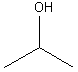
7. Alcohols
Examples:
|
CH3OH |
CH3CH2OH |
|
? |
|
methanol |
ethanol |
2-propanol |
3-methyl-3-pentanol |
|
0 o |
1 o |
2 o |
3 o |
8. Amines
Examples:
|
? |
|
? |
|
ethylamine |
dipropylamine |
trimethylamine |
9.
Ethers:
Examples:
|
CH3OCH3 |
? |
|
|
dimethyl
ether |
diethyl
ether |
ethylpropyl
ether |
Since nitrogen is a central atom, the order of the amine is
defined by the number of carbons directly attached to the nitrogen. What is the order of each the above amines?
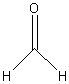
10. Aldehydes
Examples:
|
|
? |
|
|
methanal
(formaldehyde) |
propanal |
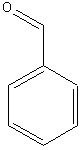
benzaldehyde |
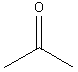
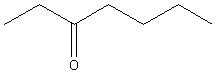
11. Ketones:
Examples:
|
|
|
? |
|
2-propanone(acetone) |
3-heptanone |
4-dodecanone |
12.
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
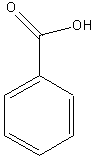
a. Carboxylic
Acid
Examples:
|
|
? |
|
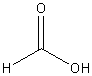
|
methanoic
acid (formic acid) |
ethanoic
acid (acetic acid) |
benzoic
acid |
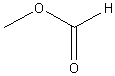
b. Esters
Examples:
|
|
? |
|
methyl
formate (methyl methanoate) |
ethyl
hexanoate |
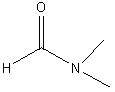
c. Amides
Examples:
|
|
|
dimethyl
formate (DMF, N,N-dimethyl methanoate) |
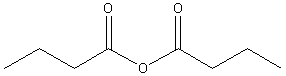
d. Anhydrides:
Examples:
|
? |
|
|
acetic
anhydride (ethanoic
anhydride) |
butanoic
anhydride |
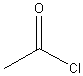
e. Acyl Halides:
Examples:
|
|
? |
|
acetylchloride (ethanoyl chloride) |
propanoyl
bromide |
f. Nitriles:
Examples:
|
? |
|
|
acetonitrile
(ethanenitrile) |
butanenitrile |
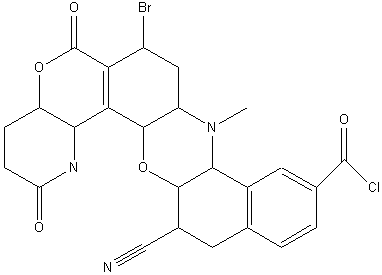
Identify all the functional groups in the following molecule&
.